PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space
Introduction
This paper builds off of ideas from PointNet (Qi et al., 2017). The name PointNet is derived from the network's input - a point cloud. A point cloud is a set of three dimensional points that each have coordinates [math]\displaystyle{ (x,y,z) }[/math]. These coordinates usually represent the surface of an object. For example, a point cloud describing the shape of a torus is shown below.
Processing point clouds is important in applications such as autonomous driving where point clouds are collected from an onboard LiDAR sensor. These point clouds can then be used for object detection. However, point clouds are challenging to process because:
- They are unordered. If [math]\displaystyle{ N }[/math] is the number of points in a point cloud, then there are [math]\displaystyle{ N! }[/math] permutations that the point cloud can be represented.
- The spatial arrangement of the points contains useful information, thus it needs to be encoded.
- The function processing the point cloud needs to be invariant to transformations such as rotation and translations of all points.
Previously, typical point cloud processing methods handled the challenges of point clouds by transforming the data with a 3D voxel grid or by representing the point cloud with multiple 2D images. When PointNet was introduced, it was novel because it directly took points as its input. PointNet++ improves on PointNet by using a hierarchical method to better capture local structures of the point cloud.

Review of PointNet
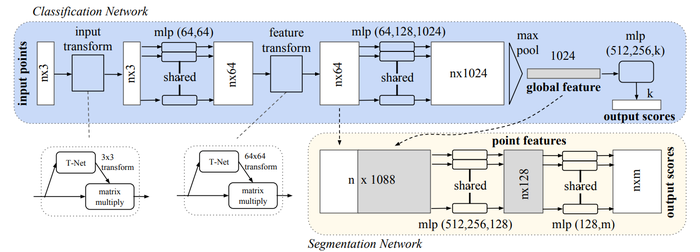
The PointNet architecture is shown below. The core idea of the network is to apply a symmetric function on transformed points. Points are transformed to handle invariance with point cloud transformations, and this transformation is represented by the multi-layer perception network and T-Net. The symmetric function solves the challenge imposed by having unordered points; a symmetric function will produce the same value no matter the order of the input. This symmetric function is represented by the max pool layer.
]
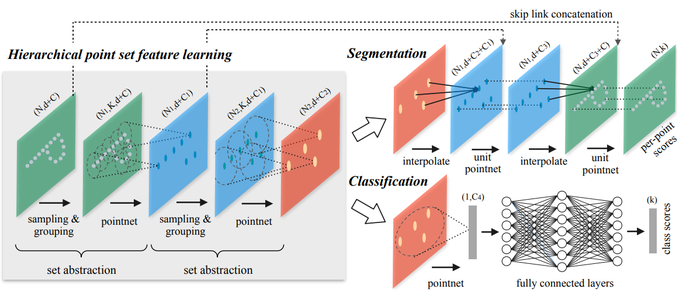
PointNet++
Problem Statement
Method
]
Sampling Layer
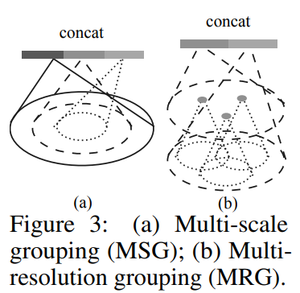
Grouping Layer
]
PointNet Layer
Robust Feature Learning under Non-Uniform Sampling Density
Experiments
Sources
1. Charles R. Qi, Li Yi, Hao Su, Leonidas J. Guibas. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space, 2017
2. Charles R. Qi, Hao Su, Kaichun Mo, Leonidas J. Guibas. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation, 2017