CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF SELF-SUPERVISION
Presented by
Maral Rasoolijaberi
Introduction
This paper presents
Previous Work
Motivation
ILSVRC 2014 Challenge Results
The proposed architecture was implemented through a deep network called GoogLeNet as a submission for ILSVRC14’s Classification Challenge and Detection Challenge.
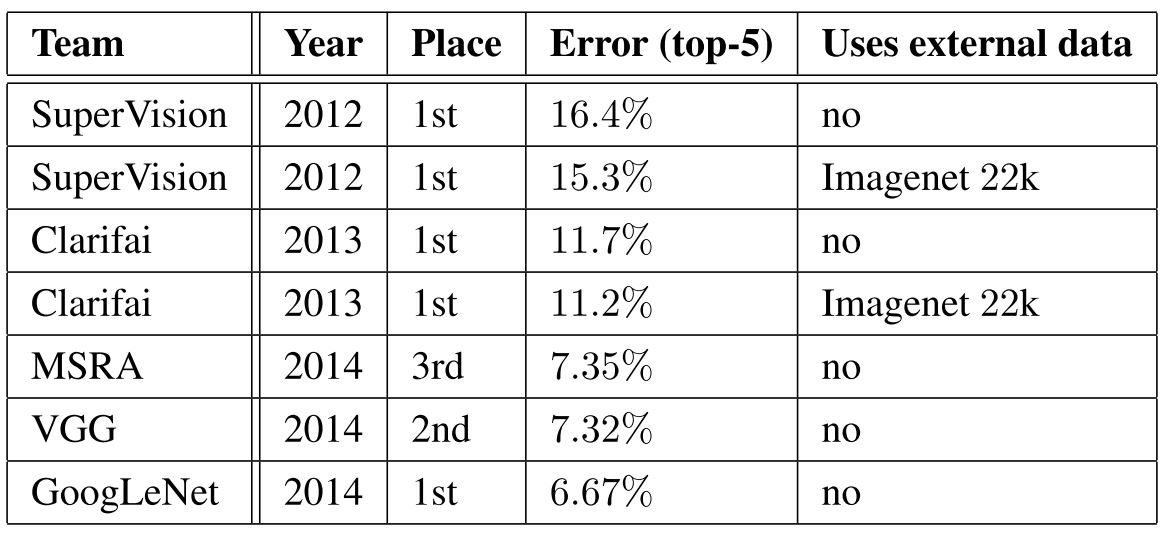
The classification challenge is to classify images into one of 1000 categories in the Imagenet hierarchy. The top-5 error rate - the percentage of test examples for which the correct class is not in the top 5 predicted classes - is used for measuring accuracy. The results of the classification challenge is shown in Table 1. The final submission of GoogLeNet obtains a top-5 error of 6.67% on both the validation and testing data, ranking first among all participants, significantly outperforming top teams in previous years, and not utilizing external data.
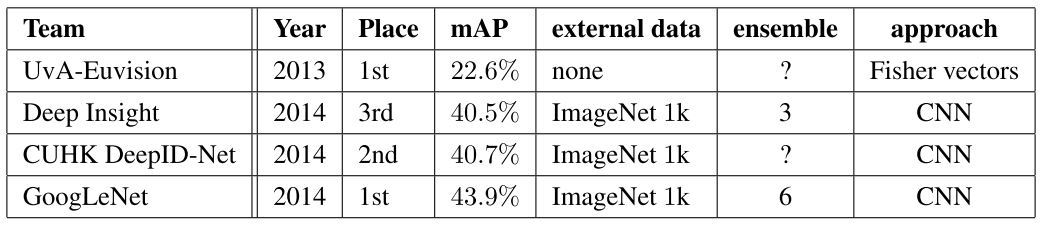
The ILSVRC detection challenge asks to produce bounding boxes around objects in images among 200 classes. Detected objects count as correct if they match the class of the groundtruth and their bounding boxes overlap by at least 50%. Each image may contain multiple objects (with different scales) or none. The mean average precision (mAP) is used to report performance. The results of the detection challenge is listed in Table 2. Using the Inception model as a region classifier, combining Selective Search and using an ensemble of 6 CNNs, GoogLeNet gave top detection results, almost doubling accuracy of the the 2013 top model.
Conclusion
Googlenet outperformed the other previous deep learning networks, and it became a proof of concept that approximating the expected optimal sparse structure by readily available dense building blocks (or the inception modules) is a viable method for improving the neural networks in computer vision. The significant quality gain is at a modest increase for the computational requirement is the main advantage for this method. Even without performing any bounding box operations to detect objects, this architecture gained a significant amount of quality with a modest amount of computational resources.
Critiques
By using nearly 5 million parameters, GoogLeNet represented nearly a 12 times reduction in terms of parameters compared it the previous architectures like VGGNet, AlexNet. This enabled Inception network to be used for many big data applications where a huge amount of data was needed to be processed at a reasonable cost while the computational capacity was limited. However, the inception network is still complex and susceptible to scaling. If the network is scaled up, large parts of the computational gains can be lost immediately. Also there was no clear description about the various factors that lead to the design decision of this inception architecture, making it harder to adapt to other applications while maintaining the same computational efficiency.
References
[1] Min Lin, Qiang Chen, and Shuicheng Yan. Network in network. CoRR, abs/1312.4400, 2013.
[2] Ross B. Girshick, Jeff Donahue, Trevor Darrell, and Jitendra Malik. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014. CVPR 2014. IEEE Conference on, 2014.
[3] Sanjeev Arora, Aditya Bhaskara, Rong Ge, and Tengyu Ma. Provable bounds for learning some deep representations. CoRR, abs/1310.6343, 2013.
[4] ¨Umit V. C¸ ataly¨urek, Cevdet Aykanat, and Bora Uc¸ar. On two-dimensional sparse matrix partitioning: Models, methods, and a recipe. SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 32(2):656–683, February 2010.
Footnote 1: Hebbian theory is a neuroscientific theory claiming that an increase in synaptic efficacy arises from a presynaptic cell's repeated and persistent stimulation of a postsynaptic cell. It is an attempt to explain synaptic plasticity, the adaptation of brain neurons during the learning process.
Footnote 2: Fore more explanation on 1 by 1 convolution refer to: https://iamaaditya.github.io/2016/03/one-by-one-convolution/