Zero-Shot Visual Imitation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The dominant paradigm for imitation learning relies on strong supervision of expert actions to learn both ''what'' and ''how'' to imitate for a certain task. For example, in the robotics field, Learning from Demonstration (LfD) (Argall et al., 2009; Ng & Russell, 2000; Pomerleau, 1989; Schaal, 1999) requires an expert to manually move robot joints (kinesthetic teaching) or teleoperate the robot to teach a desired task. The expert will, in general, provide multiple demonstrations of a specific task at training time which the agent will form into observation-action pairs to then distill into a policy for performing the task. In the case of demonstrations for a robot, this heavily supervised process is tedious and unsustainable especially looking at the fact that new tasks need a set of new demonstrations for the robot to learn from. | The dominant paradigm for imitation learning relies on strong supervision of expert actions to learn both ''what'' and ''how'' to imitate for a certain task. For example, in the robotics field, Learning from Demonstration (LfD) (Argall et al., 2009; Ng & Russell, 2000; Pomerleau, 1989; Schaal, 1999) requires an expert to manually move robot joints (kinesthetic teaching) or teleoperate the robot to teach a desired task. The expert will, in general, provide multiple demonstrations of a specific task at training time which the agent will form into observation-action pairs to then distill into a policy for performing the task. In the case of demonstrations for a robot, this heavily supervised process is tedious and unsustainable especially looking at the fact that new tasks need a set of new demonstrations for the robot to learn from. | ||
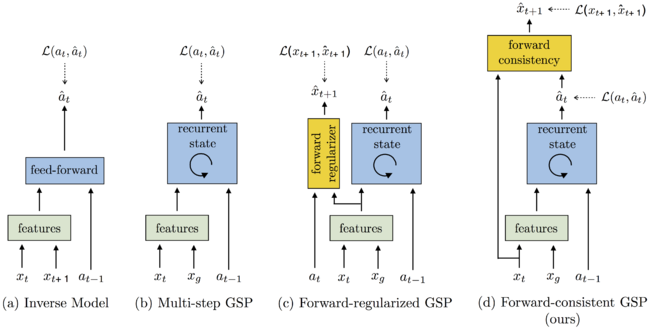
[[File:1-GSP.png | 650px|thumb|center|Figure 1: == The goal-conditioned skill policy (GSP) takes as input the current and goal observations and outputs an action sequence that would lead to that goal. We compare the performance of the following GSP models: (a) Simple inverse model; (b) Mutli-step GSP with previous action history; (c) Mutli-step GSP with previous action history and a forward model as regularizer, but no forward consistency; (d) Mutli-step GSP with forward consistency loss proposed in this work. == | [[File:1-GSP.png | 650px|thumb|center|Figure 1: == The goal-conditioned skill policy (GSP) takes as input the current and goal observations and outputs an action sequence that would lead to that goal. We compare the performance of the following GSP models: (a) Simple inverse model; (b) Mutli-step GSP with previous action history; (c) Mutli-step GSP with previous action history and a forward model as regularizer, but no forward consistency; (d) Mutli-step GSP with forward consistency loss proposed in this work. ==]] | ||
===Learning the Goal-Conditioned Skill Policy (GSP)=== | ===Learning the Goal-Conditioned Skill Policy (GSP)=== | ||
Revision as of 22:44, 31 October 2018
This page contains a summary of the paper "Zero-Shot Visual Imitation" by Pathak, D., Mahmoudieh, P., Luo, G., Agrawal, P. et al. It was published at the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) in 2018.
Introduction
The dominant paradigm for imitation learning relies on strong supervision of expert actions to learn both what and how to imitate for a certain task. For example, in the robotics field, Learning from Demonstration (LfD) (Argall et al., 2009; Ng & Russell, 2000; Pomerleau, 1989; Schaal, 1999) requires an expert to manually move robot joints (kinesthetic teaching) or teleoperate the robot to teach a desired task. The expert will, in general, provide multiple demonstrations of a specific task at training time which the agent will form into observation-action pairs to then distill into a policy for performing the task. In the case of demonstrations for a robot, this heavily supervised process is tedious and unsustainable especially looking at the fact that new tasks need a set of new demonstrations for the robot to learn from.