CapsuleNets: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
Building on this idea of hierarchical representation of spatial relationships between key entities within an image, the authors introduce Capsule Networks. Unlike traditional CNNs, Capsule Networks are better equipped to classify correctly under rotational invariance. Furthermore, the authors managed to achieve state of the art results on MNIST using a fraction of the training samples that alternative state of the art networks require. | Building on this idea of hierarchical representation of spatial relationships between key entities within an image, the authors introduce Capsule Networks. Unlike traditional CNNs, Capsule Networks are better equipped to classify correctly under rotational invariance. Furthermore, the authors managed to achieve state of the art results on MNIST using a fraction of the training samples that alternative state of the art networks require. | ||
=Background, Notations, and Definitions= | =Background, Notations, and Definitions= | ||
Revision as of 02:37, 19 November 2018
The paper "Dynamic Routing Between Capsules" was written by three researchers at Google Brain: Sara Sabour, Nicholas Frosst, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. This paper was published and presented at the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017) in Long Beach, California. The same three researchers recently published a highly related paper "Matrix Capsules with EM Routing" for ICLR 2018.
Motivation
Ever since AlexNet eclipsed the performance of competing architectures in the 2012 ImageNet challenge, convolutional neural networks have maintained their dominance in computer vision applications. Despite the recent successes and innovations brought about by convolutional neural networks, some assumptions made in these networks are perhaps unwarranted and deficient. Using a novel neural network architecture, the authors create CapsuleNets, a network that they claim is able to learn image representations in a more robust, human-like manner. With only a 3 layer capsule network, they achieved near state-of-the-art results on MNIST.
Adversarial Examples
First discussed by Christian Szegedy et. al. in late 2013, adversarial examples have been heavily discussed by the deep learning community as a potential security threat to AI learning. Adversarial examples are defined as inputs that an attacker creates intentionally fool a machine learning model. An example of an adversarial example is shown below:
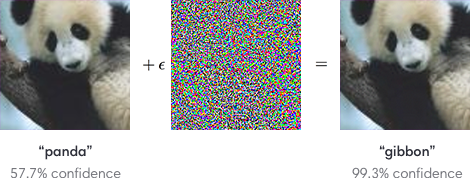
To the human eye, the image appears to be a panda both before and after noise is injected into the image, whereas the trained ConvNet model discerns the noisy image as a Gibbon with almost 100% certainty. The fact that the network is unable to classify the above image as a panda after the epsilon perturbation leads to many potential security risks in AI dependent systems such as self-driving vehicles. Although various methods have been suggested to combat adversarial examples, robust defences are hard to construct due to the inherent difficulties in constructing theoretical models for the adversarial example crafting process. However, beyond the fact that these examples may serve as a security threat, it emphasizes that these convolutional neural networks do not learn image classification/object detection patterns the same way that a human would. Rather than identifying the core features of a panda such as: its eyes, mouth, nose, and the gradient changes in its black/white fur, the convolutional neural network seems to be learning image representations in a completely different manner. Deep learning researchers often attempt to model neural networks after human learning, and it is clear that further steps must be taken to robustify ConvNets against targeted noise perturbations.
Drawbacks of CNNs
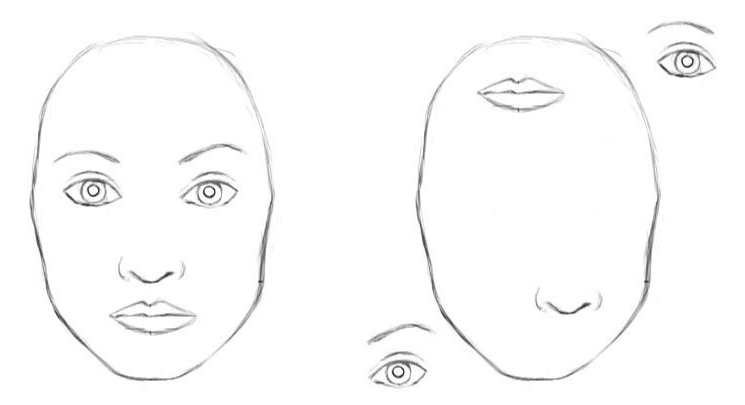
Hinton claims that the key fault with traditional CNNs lies within the pooling function. Although pooling builds translational invariance into the network, it fails to preserve spatial relationships between objects. When we pool, we effectively reduce a kxk kernel of convolved cells into a scalar input. This results in a desired local invariance without inhibiting the network's ability to detect features, but causes valuable spatial information to be lost.
In the example below, the network is able to detect the similar features (eyes, mouth, nose, etc) within both images, but fails to recognize that one image is a human face, while the other is a Picasso-esque due to the CNN's inability to encode spatial relationships after multiple pooling layers.
Conversely, we hope that a CNN can recognize that both of the following pictures contain a kitten. Unfortunately, when we feed the two images into a ResNet50 architecture, only the first image is correctly classified, while the second image is predicted to be a guinea pig.


For a more in depth discussion on the problems with ConvNets, please listen to Geoffrey Hinton's talk "What is wrong with convolutional neural nets?" given at MIT during the Brain & Cognitive Sciences - Fall Colloquium Series (December 4, 2014).
Intuition for Capsules
Human vision ignores irrelevant details by using a carefully determined sequence of fixation points to ensure that only a tiny fraction of the optic array is ever processed at the highest resolution. Hinton argues that our brains reason visual information by deconstructing it into a hierarchical representation which we then match to familiar patterns and relationships from memory. The key difference between this understanding and the functionality of CNNs is that recognition of an object should not depend on the angle from which it is viewed.
To enforce rotational and translational equivariance, Capsule Networks store and preserve hierarchical pose relationships between objects. The core idea behind capsule theory is the explicit numerical representations of relative relationships between different objects within an image. Building these relationships into the Capsule Networks model, the network is able to recognize newly seen objects as a rotated view of a previously seen object. For example, the below image shows the Statue of Liberty under five different angles. If a person had only seen the Statue of Liberty from one angle, they would be able to ascertain that all five pictures below contain the same object (just from a different angle).
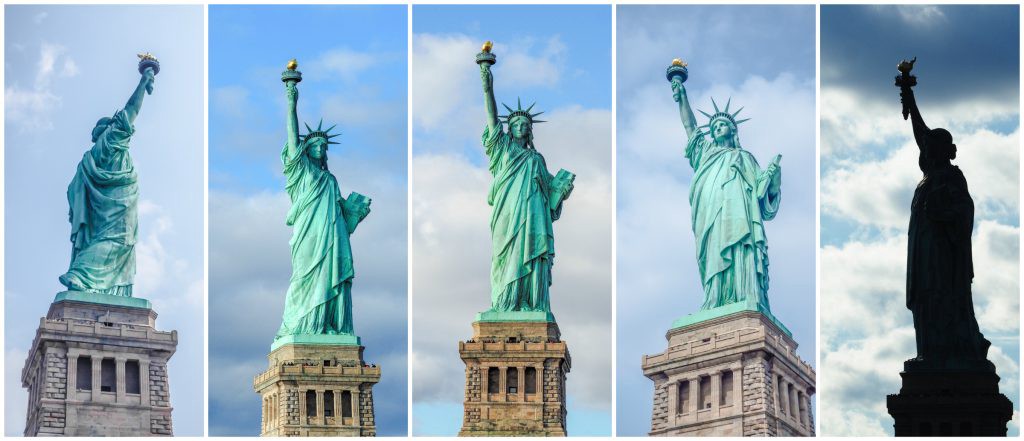

Building on this idea of hierarchical representation of spatial relationships between key entities within an image, the authors introduce Capsule Networks. Unlike traditional CNNs, Capsule Networks are better equipped to classify correctly under rotational invariance. Furthermore, the authors managed to achieve state of the art results on MNIST using a fraction of the training samples that alternative state of the art networks require.