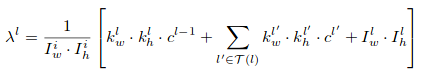stat946w18/Rethinking the Smaller-Norm-Less-Informative Assumption in Channel Pruning of Convolutional Layers: Difference between revisions
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
With the recent and ongoing surge in low-power, intelligent agents (such as wearables, smartphones, and IoT devices), there exists a growing need for machine learning models to work well in memory- and cpu-constrained environments. Deep learning models have achieved state-of-the-art on a broad range of tasks; however, they are difficult to deploy in their original forms. For example, AlexNet (Krizhevsky et al., 2012), a model for image classification, contains 61 million parameters and requires 1.5 billion FLOPs in one inference pass. A more accurate model, ResNet-50 (He et al., 2016), has 25 million parameters but requires 4.08 billion FLOPs. Clearly, it would be difficult to deploy and run these models on low-power devices. | With the recent and ongoing surge in low-power, intelligent agents (such as wearables, smartphones, and IoT devices), there exists a growing need for machine learning models to work well in memory- and cpu-constrained environments. Deep learning models have achieved state-of-the-art on a broad range of tasks; however, they are difficult to deploy in their original forms. For example, AlexNet (Krizhevsky et al., 2012), a model for image classification, contains 61 million parameters and requires 1.5 billion FLOPs in one inference pass. A more accurate model, ResNet-50 (He et al., 2016), has 25 million parameters but requires 4.08 billion FLOPs. Clearly, it would be difficult to deploy and run these models on low-power devices. | ||
In general, model compression can be accomplished using four main non-exclusive methods (Cheng et al., 2017): weight pruning, quantization, matrix transformations, and weight tying. Ye et al. (2018) explores pruning entire channels in a convolutional neural network. Past work has mostly focused on norm- or error-based heuristics to prune channels; instead, Ye et al. (2018) show that their approach is, "mathematically appealing from an optimization perspective and easy to reproduce" (Ye et al., 2018). In other words, they argue that the norm-based assumption is not as informative or theoretically justified as their approach, and provide strong empirical findings. | In general, model compression can be accomplished using four main non-exclusive methods (Cheng et al., 2017): weight pruning, quantization, matrix transformations, and weight tying. By non-exclusive we mean that these methods can be used in combination for pruning a single model; The use of one method does not exclude any of the other methods from being viable. | ||
Ye et al. (2018) explores pruning entire channels in a convolutional neural network. Past work has mostly focused on norm- or error-based heuristics to prune channels; instead, Ye et al. (2018) show that their approach is, "mathematically appealing from an optimization perspective and easy to reproduce" (Ye et al., 2018). In other words, they argue that the norm-based assumption is not as informative or theoretically justified as their approach, and provide strong empirical findings. | |||
== Motivation == | == Motivation == | ||
Revision as of 20:05, 1 March 2018
Introduction
With the recent and ongoing surge in low-power, intelligent agents (such as wearables, smartphones, and IoT devices), there exists a growing need for machine learning models to work well in memory- and cpu-constrained environments. Deep learning models have achieved state-of-the-art on a broad range of tasks; however, they are difficult to deploy in their original forms. For example, AlexNet (Krizhevsky et al., 2012), a model for image classification, contains 61 million parameters and requires 1.5 billion FLOPs in one inference pass. A more accurate model, ResNet-50 (He et al., 2016), has 25 million parameters but requires 4.08 billion FLOPs. Clearly, it would be difficult to deploy and run these models on low-power devices.
In general, model compression can be accomplished using four main non-exclusive methods (Cheng et al., 2017): weight pruning, quantization, matrix transformations, and weight tying. By non-exclusive we mean that these methods can be used in combination for pruning a single model; The use of one method does not exclude any of the other methods from being viable.
Ye et al. (2018) explores pruning entire channels in a convolutional neural network. Past work has mostly focused on norm- or error-based heuristics to prune channels; instead, Ye et al. (2018) show that their approach is, "mathematically appealing from an optimization perspective and easy to reproduce" (Ye et al., 2018). In other words, they argue that the norm-based assumption is not as informative or theoretically justified as their approach, and provide strong empirical findings.
Motivation
Some previous work on pruning channel filters (Li et al., 2016; Molchanov et al., 2016) have focused on using the L1 norm to determine the importance of a channel. Ye et al. (2018) show that, in the deep linear convolution case, penalizing the per-layer norm is coarse-grained; the impact on the total loss is difficult to measure. Consider the loss with LASSO:
$$\min \mathbb{E}_D \lVert W_n * \dots * W_1 x - y\rVert^2 + \lambda \sum_{i=1}^n \lVert W_i \rVert_1$$
where W are the weights and * is convolution. Ye et al. (2018) show that, by multiplying and dividing subsets of the weights by some constant, it is always possible to reduce the loss without norm penalization. Furthermore, batch normalization (Ioffe, 2015) is incompatible with this method of weight regularization. In other words, penalizing the norm of a filter in a deep convolutional network is hard to justify from a theoretical perspective.
Thus, although not providing a complete theoretical guarantee on loss, Ye et al. (2018) develop a pruning technique that claims to be more justified than norm-based pruning is.
Method
At a high level, Ye et al. (2018) propose that, instead of discovering sparsity via penalizing the per-filter or per-channel norm, penalize the batch normalization scale parameters gamma instead. The reasoning is that by having fewer parameters to constrain and working with normalized values, sparsity is easier to enforce, monitor, and learn. Having sparse batch normalization terms has the effect of pruning entire channels: if gamma is zero, then the output at that layer becomes constant (the bias term), and thus the preceding channels can be pruned.
Summary
The basic algorithm can be summarized as follows:
1. Penalize the L1-norm of the batch normalization scaling parameters in the loss
2. Train until loss plateaus
3. Remove channels that correspond to a downstream zero in batch normalization
4. Fine-tune the pruned model using regular learning
Details
There still exist a few problems that this summary has not addressed so far. Sub-gradient descent is known to have inverse square root convergence rate on subdifferentials (Gordon et al., 2012), so the sparsity gradient descent update may be suboptimal. Furthermore, the sparse penalty needs to be normalized with respect to previous channel sizes, since the penalty should be roughly equally distributed across all convolution layers.
Slow Convergence
To address the issue of slow convergence, Ye et al. (2018) use an iterative shrinking-thresholding algorithm (ISTA) (Beck & Teboulle, 2009) to update the batch normalization scale parameter. The intuition for ISTA is that the structure of the optimization objective can be taken advantage of; consider $$L(x) = f(x) + g(x)$$
Let f be the model loss and g be the non-differentiable penalty (LASSO). ISTA is able to use the structure of the loss and converge in O(1/n), instead of O(1/sqrt(n)) when using subgradient descent, which assumes no structure about the loss. Even though ISTA is used in convex settings, Ye et. al (2018) argue that it still performs better than gradient descent.
Penalty Normalization
In the paper, Ye et al. (2018) normalize the per-layer sparse penalty with respect to the global input size, the current layer kernel areas, the previous layer kernel areas, and the local input feature map area.
To control the global penalty, a hyperparamter rho is multiplied with all the per-layer lambda in the final loss.
Steps
The final algorithm can be summarized as follows:
1. Compute the per-layer normalized sparse penalty constant lambda
2. Compute the global LASSO loss with global scaling constant rho
3. Until convergence, train scaling parameters using ISTA and non-scaling parameters using regular gradient descent.
4. Remove channels that correspond to a downstream zero in batch normalization
5. Fine-tune the pruned model using regular learning
Results
The authors show state-of-the-art performance, compared with other channel-pruning approaches. It is important to note that it would be unfair to compare against general pruning approaches; channel pruning specifically removes channels without introducing intra-kernel sparsity, whereas other pruning approaches introduce irregular kernel sparsity and hence computational inefficiencies.
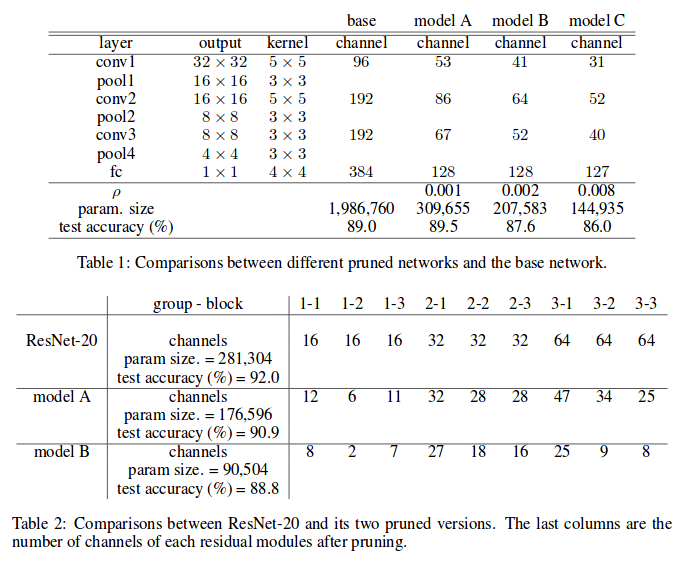
Results on CIFAR-10:
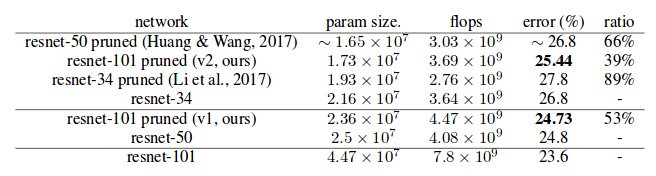
Results on ILSVRC2012:
Conclusion
Pruning large neural architectures to fit on low-power devices is an important task. It would be interesting to conduct actual power measurements on the pruned models vs baseline for a real quantitative measure of efficiency; reduction in FLOPs doesn't necessarily correspond with vastly reduced power, since memory accesses dominate energy consumption (Han et al., 2015). However, the reduction in number of FLOPs and parameters is encouraging, so moderate power savings should be expected.
It would also be interesting to combine multiple approaches, or "throw the whole kitchen sink" at this task. Han et al. (2015) sparked much recent interest by successfully combining weight pruning, quantization, and Huffman coding without loss in accuracy. However, their approach introduced irregular sparsity in the convolutional layers, so a direct comparison cannot be made.
In conclusion, this novel, theoretically-motivated interpretation of channel pruning was successfully applied to several important tasks.
References
- Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2012). Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 1097-1105).
- He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 770-778).
- Cheng, Y., Wang, D., Zhou, P., & Zhang, T. (2017). A Survey of Model Compression and Acceleration for Deep Neural Networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.09282.
- Ye, J., Lu, X., Lin, Z., & Wang, J. Z. (2018). Rethinking the Smaller-Norm-Less-Informative Assumption in Channel Pruning of Convolution Layers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.00124.
- Li, H., Kadav, A., Durdanovic, I., Samet, H., & Graf, H. P. (2016). Pruning filters for efficient convnets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.08710.
- Molchanov, P., Tyree, S., Karras, T., Aila, T., & Kautz, J. (2016). Pruning convolutional neural networks for resource efficient inference.
- Ioffe, S., & Szegedy, C. (2015, June). Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 448-456).
- Gordon, G., & Tibshirani, R. (2012). Subgradient method. https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~ggordon/10725-F12/slides/06-sg-method.pdf
- Beck, A., & Teboulle, M. (2009). A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM journal on imaging sciences, 2(1), 183-202.
- Han, S., Mao, H., & Dally, W. J. (2015). Deep compression: Compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and huffman coding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1510.00149