goingDeeperWithConvolutions: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Introduction = | = Introduction = | ||
In the last three years, due to the advances of deep learning and more concretely convolutional networks. [http://white.stanford.edu/teach/index.php/An_Introduction_to_Convolutional_Neural_Networks [an introduction of CNN]] , the quality of image recognition has increased dramatically. The error rates for ILSVRC competition dropped significantly year by year.[http://image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/ [LSVRC]] This paper proposed a new deep convolutional neural network architecture codenamed Inception. With the inception module and carefully crafted design researchers build a 22 layers deep network called Google Lenet, which uses 12X fewer parameters while being significantly more accurate than the winners of ILSVRC 2012.<ref> | In the last three years, due to the advances of deep learning and more concretely convolutional networks. [http://white.stanford.edu/teach/index.php/An_Introduction_to_Convolutional_Neural_Networks [an introduction of CNN]] , the quality of image recognition has increased dramatically. The error rates for ILSVRC competition dropped significantly year by year.[http://image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/ [LSVRC]] This paper<ref> | ||
Szegedy, Christian, et al. [http://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.4842.pdf "Going deeper with convolutions."] arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.4842 (2014). | |||
</ref> proposed a new deep convolutional neural network architecture codenamed Inception. With the inception module and carefully crafted design researchers build a 22 layers deep network called Google Lenet, which uses 12X fewer parameters while being significantly more accurate than the winners of ILSVRC 2012.<ref> | |||
Krizhevsky, Alex, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. [http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~fritz/absps/imagenet.pdf "Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks."] | Krizhevsky, Alex, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. [http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~fritz/absps/imagenet.pdf "Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks."] | ||
Advances in neural information processing systems. 2012. | Advances in neural information processing systems. 2012. | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 20 October 2015
Introduction
In the last three years, due to the advances of deep learning and more concretely convolutional networks. [an introduction of CNN] , the quality of image recognition has increased dramatically. The error rates for ILSVRC competition dropped significantly year by year.[LSVRC] This paper<ref> Szegedy, Christian, et al. "Going deeper with convolutions." arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.4842 (2014). </ref> proposed a new deep convolutional neural network architecture codenamed Inception. With the inception module and carefully crafted design researchers build a 22 layers deep network called Google Lenet, which uses 12X fewer parameters while being significantly more accurate than the winners of ILSVRC 2012.<ref> Krizhevsky, Alex, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. "Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks."
Advances in neural information processing systems. 2012.
</ref>
Related work
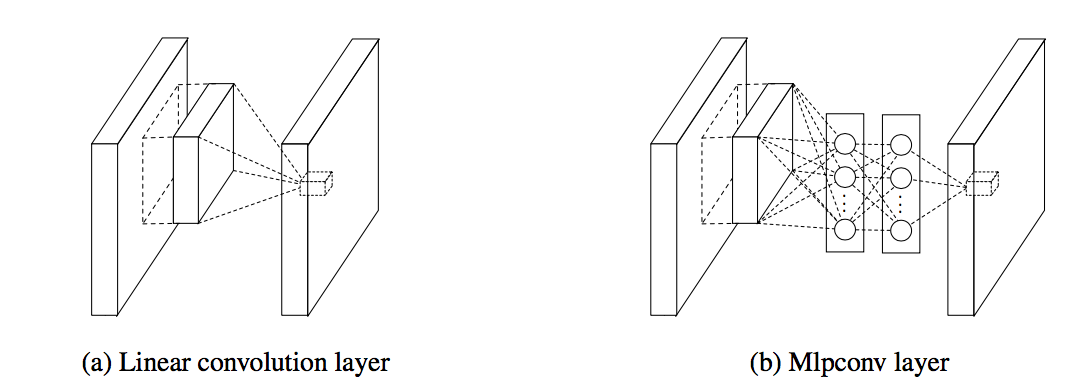
In 2013 Lin et al.<ref> Min Lin, Qiang Chen and Shuicheng Yan. Network in Network </ref> pointed out that the convolution filter in CNN is a generalized linear model (GLM) for the underlying data patch and the level of abstraction is low with GLM. They suggested replacing GLM with a ”micro network” structure which is a general nonlinear function approximator.
References
<references />