SPINS Tutorial
This is a tutorial for getting up to speed with SPINS using the case mode1_mode2. The first part of the tutorial discusses running the case with the default parameters, some basic analysis tools and techniques, and manually changing parameters. The second part of the tutorial explores more parameter combinations using Matlab driver scripts to automate the workflow. The final part using a Matlab script spins_refinement.m to interpolate an existing SPINS output onto a finer grid and restart SPINS at higher resolution.
You must first have followed the instructions to install SPINS and compile the case file.
Part 1: Getting familiar with SPINS
Run
Transfer the executable (mode1_mode2.x) and the configuration file (spins.conf) into a clean directory.
Run simulation by executing mpirun -np 4 ./mode1_mode2.x on the command line, or submit the job to the queue on a Compute Canada system with a submit script (see submitting jobs to Graham).
This will create two types of files
- Output files
- These are of the form
rho.3where the name (rho) is the variable and the extension is the output number
- - For example rho.3 is the density field at output number 3. Zero-indexing is used, so this is the 4th density file
- Since these can be memory expensive, they are created relatively infrequently
- These are of the form
- Diagnostic files
- These will generally be text files and contain information about the simulation
- Matlab plotters for the diagnostic files are found in the SPINSmatlab toolbox (preinstalled on boogaloo).
| Diagnostic Files | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| File | Optional | Matlab plotter | Description |
| diagnostics.txt | No | plot_diagnos | High temporal resolution information about the simulation (occurs at every time step). Examples include: KE, max velocity, energy budget terms, simulation timings. |
| stresses_top.txt and/or stresses_bottom.txt | Yes | plot_stress | Surface forces and surface stress extrema at the top/bottom surfaces. Only applicable if no slip boundary condition is used. |
| plot_times.txt | No | plot_diagnos | Explicit statement of the time associated with each output. Also gives the time to write output files. |
Analyze
Matlab and Python are the primary languages used for analyzing SPINS simulations. These are great for computation of quantities specific to your study. The Python (SPINSpy) and Matlab (SPINSmatlab) packages contain much of the important tools for each language. Three dimensional visualization should use Paraview or VisIt (see Visualization).
Here, we will use Matlab to make a simple plot of the density field. We assume that the SPINSmatlab package is on your path (as is the case for boogaloo).
gdpar = spins_gridparams(); split_gdpar- This reads in the grid and parameters and places them in a structure (
gdpar).split_gdparseparates the two sub-structures into the structuresparandgd, which are the parameters and grid, respectively. parcontains information fromspins.confin addition to further simulation parametersgdcontains the grid. x,y,z grids can be extracted withgd.x,gd.y,orgd.z- The default setting is that the grid is unmapped and vector grids are produced, to get the full grid use
gdpar = spins_gridparams('FastFull');orgdpar = spins_gridparams('Full');
- This reads in the grid and parameters and places them in a structure (
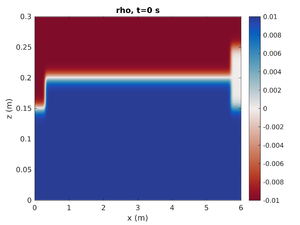
spins_plot2d('rho',0);- First argument is the field to plot
- Second argument is the output number. The simulation time can also be specified in this argument as a string.
spins_plot2d('rho','2');will plot the simulation at the closest output to t=2s. Many optional arguments exist (typehelp spins_plot2dfor more options).
To read an individual file:
u = spins_reader('u',10);
Restart
Should you need to restart the simulation (due to expenditure of allocated time, require more time, a node failure, or otherwise) simply change the restart flags in the configuration file.
The simplest change is to set
restart = true restart_time = 5.5 restart_sequence = 11
where the simulation will restart at output 11 which corresponds to t=5.5s. These numbers can be found in the last row of plot_times.txt.
SPINS also has an automatic safety dump if the allocated time is close to expiring (See automatically specify the runtime for more info). In this case, if the safety write was done successfully then you only need to set
restart_from_dump = true
Change
If after analyzing the simulation you realize that you wanted to change a parameter (it wasn't quite right), then you only need to change the parameter in the configuration file (as opposed to older editions of SPINS where you'd need to recompile the entire code).
Here is a description of the problem parameters:
--delta_rho arg Density difference between upper and lower layers (as a percentage of rho_0) --pyc_loc arg Pycnocline location --h_halfwidth arg Pycnocline half-width --delta_x arg Horizontal transition half-width --H2 arg Height of mixed region (mode-2) - sets mode-2 wave amplitude --H1 arg Heigth of mixed region (mode-1) - sets mode-1 wave amplitude --L1 arg Length of region 1 (mode-2) --L2 arg Length of region 2 (mode-1) --dye1_loc arg Location of dye 1 --dye2_loc arg Location of dye 2 --dye1_width arg Width of dye 1 --dye2_width arg Width of dye 2 --dye_halfwidth arg Sharpness of the dye transition --enable_tracer Enable evolution of second tracers
If you run the simulation in the same directory, remember to clear all simulation files (output and diagnostic files).
Only Mode-1 ISW
To change the simulation to only have the left mode-1 ISW change spins.conf to have:
H2 = 0.0
This will set the mode-2 amplitude to zero.
Only Mode-2 ISW
To change the simulation to only have the right mode-2 ISW change spins.conf to have:
H1 = 0.0
This will set the mode-1 amplitude to zero.
Gravity Current
To change the simulation to have a rightward moving gravity current change spins.conf to have:
pyc_loc = -0.2 H1 = -1.0 H2 = 0.0
This will move the pycnocline below the bottom boundary, set the mode-1 amplitude to result in a region of high density at on end of the tank, and give no mode-2 contribution.
Try it yourself. See what each parameter does when they're changed.
Part 2: Matlab driver scripts (UNDER CONSTRUCTION)
Part 2 and 3 extend the previous tutorial. In the remaining sections of this tutorial you will:
- use a text file specifying parameters for a selection of cases to automatically set up the cases and submit them all to the compute canada scheduler.
- use the matlab script `spins_refinement.m` to refine the grid for one of the above cases and restart the simulation at higher resolution from a specified timestep.
Setup
To get started on these parts, clone the SPINS refinement git repo. Move into the tutorial/ directory within SPINS-refinement.
This directory contains all the files needed to run an already designed selection of cases with no modification necessary.
Run
The workflow for using these scripts is illustrated in the workflow diagram below. Here you will walk through the process.
As mentioned above, some interesting parameters to change are H1, L1, H2, L2, and pyc_loc. The text file `mode1_mode2.txt` controls the cases we will run. Open this file and look at its contents. There are 5 cases, each with a different set of parameters:
- base. This is the base case, with the default parameters as in the original spins.conf file for this tutorial.
- mode1. This case changes the mode 2 amplitude and length to 0, meaning we will only have a mode 1 wave propagating to the right.
- mode2. This case changes the mode 1 amplitude and length to 0, meaning we will only have a mode 2 wave propagating to the right.
- gravity. This cases uses the parameters as described above to create a gravity current.
- lamp. This cases increases the height and width of the mode 1 and mode 2 regions to create larger amplitude waves. The pycnocline is also set to be in the middle of the tank.
The matlab script driver_mode1_mode2.m sets up the cases. It creates directories for each case (named according to the casename), writes the parameters to a new spins.conf file, and creates the initial u, v, w, and rho files. This script has its own documentation on the git repository, and the code is well commented.
Now we actually run these cases.
To do this, submit the matlab.sh script to the scheduler (sbatch matlab.sh). This job runs wavereader.x and submits a job for each case. Specifically, it submits the submit.sh script from each case directory.
Designing your own cases
You can add your own cases by adding them to the text file mode1_mode.txt. The casenames in this text file must match the casenames in the matlab.sh submission script! Try adding a case to the existing list and running all the cases again.
Modifying parameters that aren't already a column in the text file is somewhat more work. You have to modify the driver_mode1_mode2.m script. First, add the parameter as a column to the text file listing the cases. Then in the driver script driver_mode1_mode.m read in this parameter from the text table and make sure it is being written to spins.conf.
There is more documentation and examples available on the SPINS-refinement repository.
Part 3: Refining the grid from existing outputs (UNDER CONSTRUCTION)
Say you ran a simulation and noticed that after a certain time, the model output began to exhibit signs of small unphysical oscillations. Or perhaps you almost managed to resolve a feature of interest near the end of your simulation. Both of these scenarios could be solved by restarting your simulation from the beginning with higher resolution, however, in the interest of time (especially for large runs), it may be useful to start from an earlier point in your existing simulation with a higher resolution.
This is where the script spins_refinement.m becomes useful. spins_refinement.m takes all the field at a specified output, makes a finer grid, and interpolates the existing outputs onto this finer grid. It then outputs new fields that can be read by wavereader.x. This effectively allows you to restart a simulation from an earlier output but with higher resolution.
Usage
The only lines that the user should have to edit are given below.
nx = 4; % nx times of original resolution in x
nz = 2; % nz times of original resolution in z
ii = 100; % number of output to interpolate
method = 'nearest'; % Matlab built-in interpolation method
% 'nearest', 'linear', 'spline' or 'cubic'
nx = 4 and nz = 2 mean that the number of grid points in the horizontal and vertical directions will be increased by a factor of 4 and 2 respectively. The line ii = 100 determined what output would the user would like to refine and begin the new simulation from.
This output will be the new initial condition for the higher resolution version of your case. Be aware that the output you choose must be sufficiently early that any transient motion due to the interpolation can be removed by viscosity or filtering before the motion of interest is analyzed.
Lastly, may also edit the variable ‘method’, which changes the interpolation method used. Currently, the only methods available are nearest, linear, spline, or cubic. In the future, a separate script for spectral interpolation may be added.