Buoyancy Frequency: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Ndiagram.png|thumb|400px|right|Forces on a fluid parcel raised by <math> z </math> from it's rest state at <math> z_0 </math>.]] | [[File:Ndiagram.png|thumb|400px|right|Forces on a fluid parcel raised by <math> z </math> from it's rest state at <math> z_0 </math>.]] | ||
Here we demonstrate that a fluid parcel oscillates around it's rest state at the buoyancy frequency. Vallis (2006) has similar derivation to the following. | Here we demonstrate that a fluid parcel oscillates around it's rest state at the buoyancy frequency. Credit to Vallis (2006) which has similar derivation to the following. | ||
Consider a stable, motionless stratification, <math> \rho(z) </math>. A fluid parcel of volume <math> V </math> at depth <math> z_0 </math> will therefore have a mass of <math> \rho(z_0) V </math>. If that parcel of fluid is adiabatically lifted by a infinitesimal amount to a depth of <math> z_0 + | Consider a stable, motionless stratification, <math> \rho(z) </math>. A fluid parcel of volume <math> V </math> at depth <math> z_0 </math> will therefore have a mass of <math> \rho(z_0) V </math>. If that parcel of fluid is adiabatically lifted by a infinitesimal amount to a depth of <math> z_0 + \zeta </math> then the fluid will experience a net downward force due to it being heavier than the surrounding fluid. | ||
By Archimedes' principle, the magnitude of the buoyancy force is equivalent to the weight of the fluid displaced by the fluid parcel. | By Archimedes' principle, the magnitude of the buoyancy force is equivalent to the weight of the fluid displaced by the fluid parcel. Ignoring all drag forces, the net force on the parcel at a depth of <math> z_0 + \zeta </math> is | ||
:<math> \begin{align} | :<math> \begin{align} | ||
F &= B-F_g\\ | F &= B-F_g\\ | ||
&= g \rho(z_0+ | &= g \rho(z_0+\zeta) V - g \rho(z_0) V\\ | ||
&= g V \left(\rho(z_0+ | &= g V \left(\rho(z_0+\zeta) - \rho(z_0)\right)\\ | ||
&= g V \left(\rho(z_0)+\frac{d\rho( | &= g V \left(\rho(z_0)+\left.\frac{d\rho(z)}{dz}\right\vert_{z=z_0}\zeta + \mathcal{O}\left( \zeta^2 \right) - \rho(z_0)\right)\\ | ||
&= g V \frac{d\rho( | &= g V \left.\frac{d\rho(z)}{dz}\right\vert_{z=z_0}\zeta + \mathcal{O}\left( \zeta^2 \right) | ||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
By Newton's second law, | By assumption, <math> \zeta \ll 1 </math>, so the higher order terms are negligible compared to the first. Therefore, Newton's second law is, | ||
:<math> \begin{align} | :<math> \begin{align} | ||
\rho(z_0) V \frac{d^2 | \rho(z_0) V \frac{d^2 \zeta}{dt^2} &= g V \left.\frac{d\rho(z)}{dz}\right\vert_{z=z_0}\zeta\\ | ||
\frac{d^2 | \frac{d^2 \zeta}{dt^2} &= \frac{g}{\rho(z_0)} \left.\frac{d\rho(z)}{dz}\right\vert_{z=z_0}\zeta \\ | ||
\frac{d^2 | \frac{d^2 \zeta}{dt^2} + N^2 \zeta &= 0 \\ | ||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
where <math> N^2(z) = -\frac{g}{\rho(z)} \frac{d\rho(z)}{dz} </math>. This is simply an undamped harmonic oscillator which vibrates at a frequency of <math> N </math>. The negative sign in <math> N </math> is necessary to ensure that the buoyancy frequency is real for stable stratification. | where <math> N^2(z) = -\frac{g}{\rho(z)} \frac{d\rho(z)}{dz} </math>. This is simply an undamped harmonic oscillator which vibrates at a frequency of <math> N </math>. The negative sign in the definition of <math> N^2 </math> is necessary to ensure that the buoyancy frequency is real for stable stratification. The buoyancy frequeyncy is <math> N^2(z) = -\frac{g}{\rho_0} \frac{d\rho(z)}{dz} </math> if the Boussinesq approximation is made. | ||
Revision as of 10:55, 25 June 2015
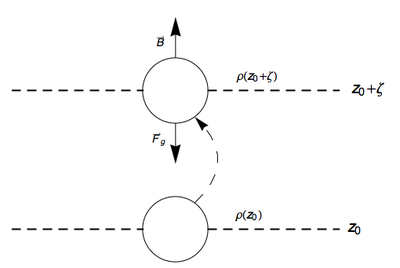
Here we demonstrate that a fluid parcel oscillates around it's rest state at the buoyancy frequency. Credit to Vallis (2006) which has similar derivation to the following.
Consider a stable, motionless stratification, . A fluid parcel of volume at depth will therefore have a mass of . If that parcel of fluid is adiabatically lifted by a infinitesimal amount to a depth of then the fluid will experience a net downward force due to it being heavier than the surrounding fluid.
By Archimedes' principle, the magnitude of the buoyancy force is equivalent to the weight of the fluid displaced by the fluid parcel. Ignoring all drag forces, the net force on the parcel at a depth of is
By assumption, , so the higher order terms are negligible compared to the first. Therefore, Newton's second law is,
where . This is simply an undamped harmonic oscillator which vibrates at a frequency of . The negative sign in the definition of is necessary to ensure that the buoyancy frequency is real for stable stratification. The buoyancy frequeyncy is if the Boussinesq approximation is made.












